Assimilation Integration Separation Marginalisation
Critical History of the Acculturation Psychology of Assimilation, Separation, Integration, and Marginalization Show all authors and why bicultural integration and marginalisation are confounded constructs There is no robust evidence that biculturalism is most adaptive References.
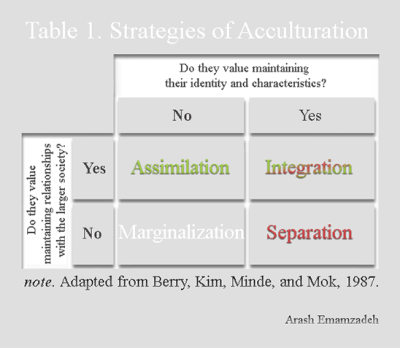
Assimilation integration separation marginalisation. * Assimilation – Where someone from a different culture adopts the cultural norm of the county/region that they have moved to (Cohen, 11, 7) * Integration – Where people adopt both the dominant culture and their original culture, combining the two at the same time (Cohen, 11, 9). Terms such as assimilation, integration, separation, segregation, marginalization, etc are used in scientific literature and the mass media to describe different types of acculturative strategies An acculturation model developed by Berry and applied by many researchers has been. According to Berry's model, a harmonisation process can result in marginalisation, separation, assimilation or integration, in which marginalisation is defined as a situation in which displaced.
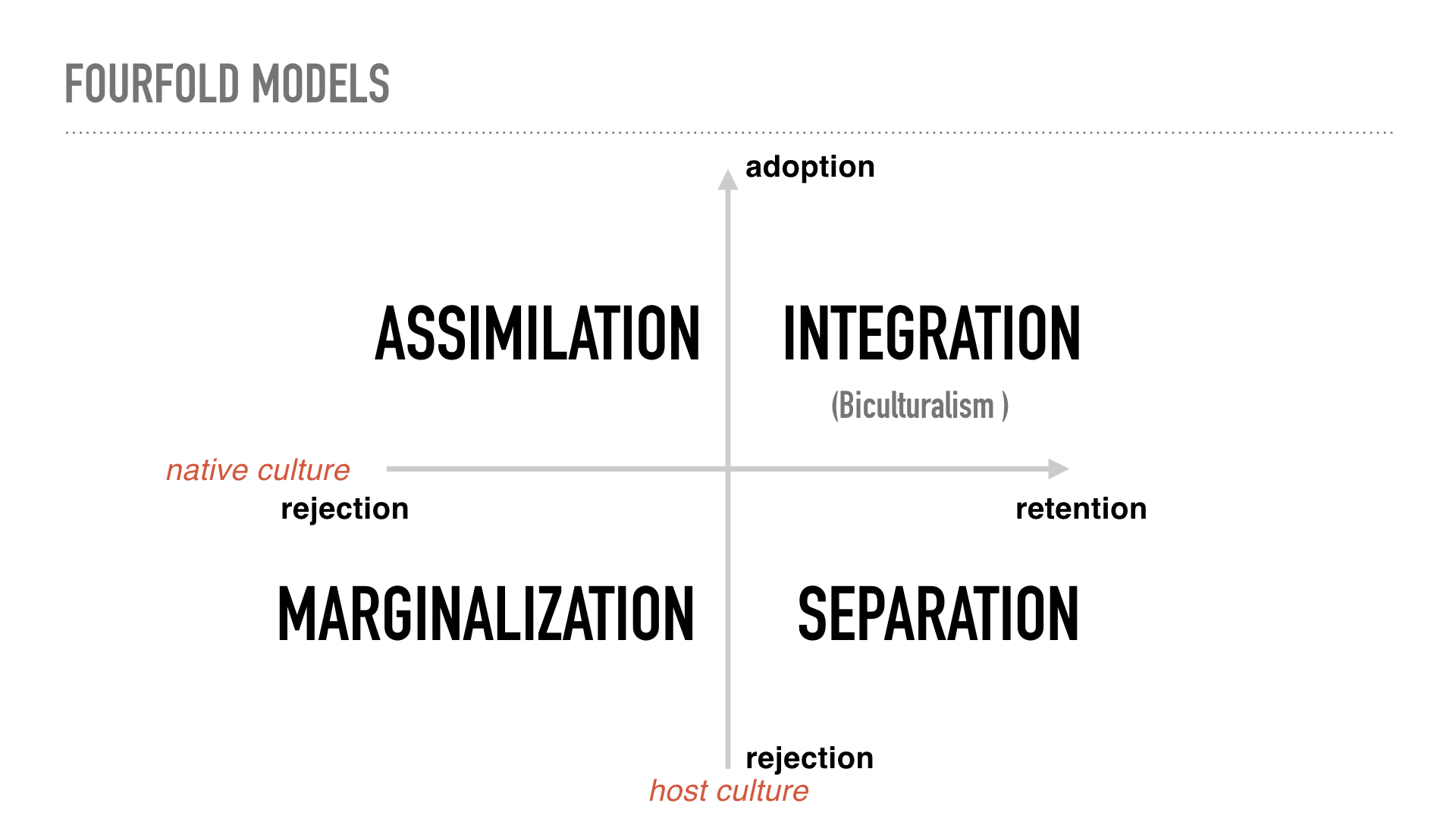
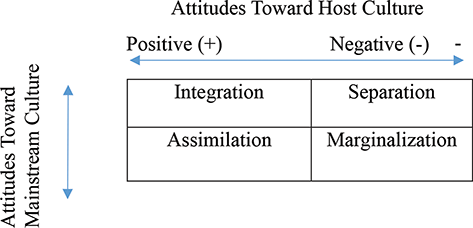
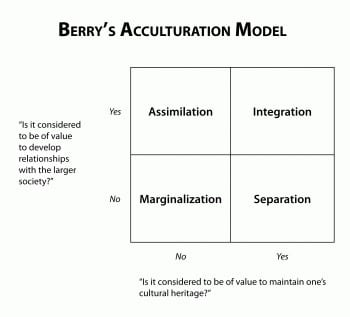
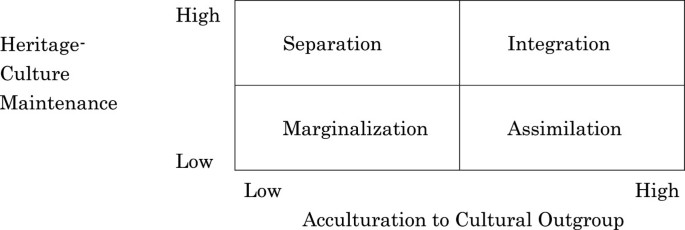
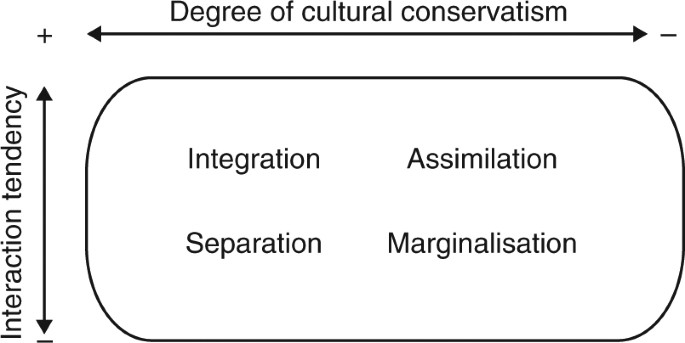
Finally, if a group or a person values both their own original culture and the culture of the majority community, conditions are met for Integration. Berry’s Acculturation Model Assimilation Integration Marginalisation Separation Reject Home Culture Retain Home Culture Accept Host Culture Reject Host Culture 10 Berry’s Acculturation Model Assimilation Integration Marginalisation Separation Reject Home Culture Retain Home Culture Accept Host Culture Reject Host Culture 11. Integration is a process where the minority cultures take something in from the majority culture to become a part of the majority culture retaining their identity Assimilation Assimilation is a process of absorbing minority communities into the ways and views of the majority community in a multicultural society.
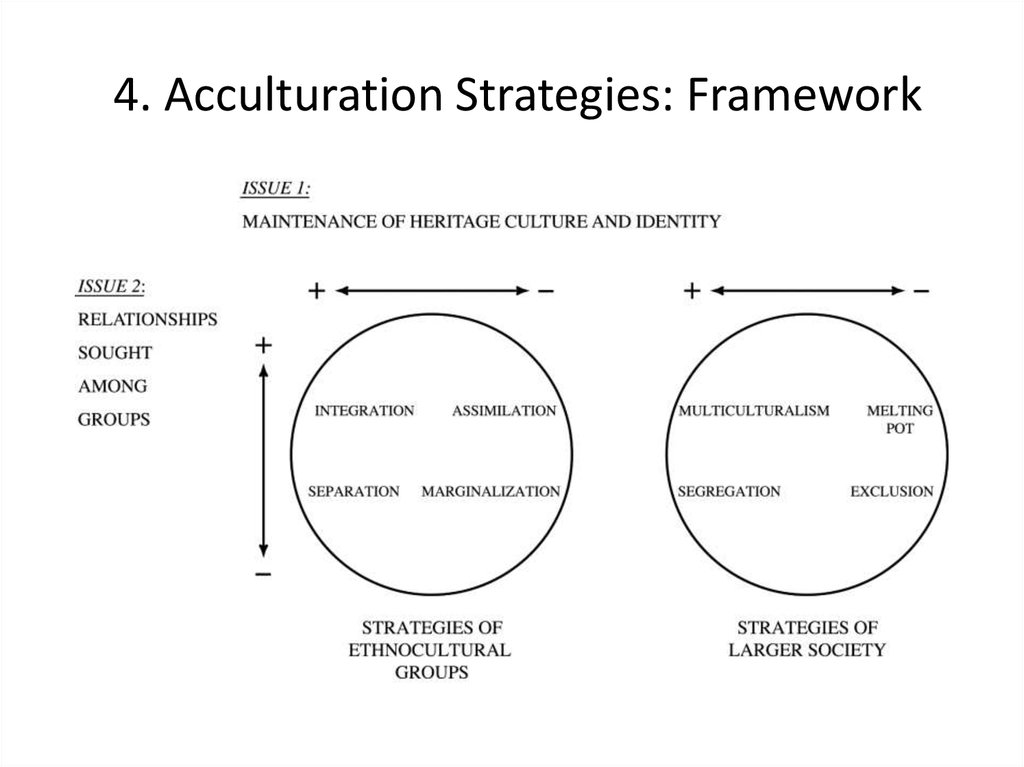
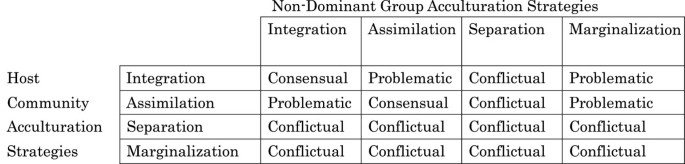
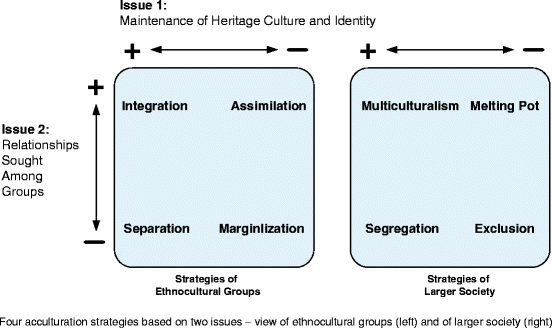
(or modes) for acculturation can be assimilation, separation, integration and marginalization (Berry, 03) In the assimilation strategy, individuals do not want to maintain their cultural identity and seek interactions with other cultural groups Alternatively, in the separation strategy, individuals. Corresponding Strategies of the Larger Society Each of the four acculturation orientations has a corresponding 'strategy' in the larger society Integration = Multiculturalism Assimilation = Melting Pot / Pressure Cooker Separation = Segregation Marginalisation = Exclusion. SeparationThe individual maintains his or her own identity and does not absorbed into host culture IntegrationThe individual that maintains his own culture and also adapts the host culture MarginalizationThe individual does not identify with or participate in either his or her own culture or host culture Much crosscultural researched has focused on acculturation.
Assimilation Integration Separation Marginalisation Berry’s acculturation model Reject Home Culture Retain Home Culture Accept Host Culture Reject Host Culture “Generally, those pursuing the integration strategy experience less stress, and achieve better adaptations than those pursuing marginalisation” (Berry, 05) (Berry, 1997). η 2 = 03). Assimilation or integration Similarities and differences between acculturation attitudes of migrants from Central Asia and Russians in Central Russia Established in 08, the Russian Psychological Society's Journal «Psychology in Russia State of the Art» publishes original articles.
Critical History of the Acculturation Psychology of Assimilation, Separation, Integration, and Marginalization Show all authors and why bicultural integration and marginalisation are confounded constructs There is no robust evidence that biculturalism is most adaptive References. Tribal policy Isolation, Assimilation and Integration Historical Perspective Isolation The coexistence of fundamentally different culture patterns and styles of living has always been a characteristic feature of the Indian stage Unlike most parts of the world, in India, the arrival of new immigrants and the spread of their way of life did. According to Berry (1997), four acculturation strategies were introduced assimilation, separation, marginalization, and integration When individuals do not wish to maintain their cultural identity and seek daily interaction with other new cultures, the assimilation strategy is defined.
Assimilation, Separation and Integration in Berry, 1997), Schumann (1986) as sumes that it is the assimilation strategy that is the best predictor of success The adaptation strategy, corresponding to Integration (“the group adapts to the. Assimilation Integration Separation Marginalisation Berry’s acculturation model Reject Home Culture Retain Home Culture Accept Host Culture Reject Host Culture “Generally, those pursuing the integration strategy experience less stress, and achieve better adaptations than those pursuing marginalisation” (Berry, 05) (Berry, 1997). DOAJ is a communitycurated online directory that indexes and provides access to high quality, open access, peerreviewed journals.
Q) Berry’s SelfAcculturation Strategies are Assimilation, Integration, Separation, and Marginalization Using John Berry’s Acculturation Strategies, First, describe your own acculturation strategy that you usually adopt when you are in a new environment Second, compare it with your acculturation experience during your first semester on the university campus (what was your strategy(s) and. Integration was the acculturation style with the highest mean values, followed by assimilation and separation with similar mean scores The means for marginalization were the lowest The results of the MANOVA revealed a main effect for gender differences in acculturation style ( F (4, 433) = 379;. Assimilation Versus SeparationJoseph the Administrator and the Politics of Religion in Biblical Israel by ron Wildavsky Transaction 236 pp $3295 To assimilate or to stay apart?.
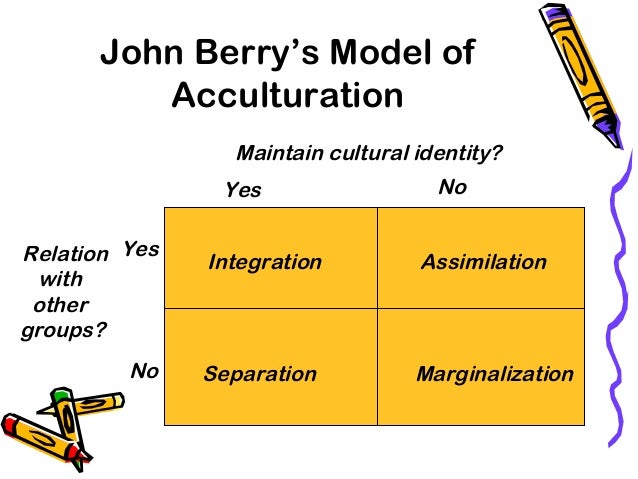
This study examined the relationship between acculturation modes (assimilation, integration, separation and marginalization), social support, and acculturative stress in undergraduate and graduate international students (N=104) at a mediumsized public university in the Midwestern United States. Culture, results in the strategy of Assimilation In the case of two ‘minuses’ a group or a person faces Marginalisation, and can be said not to feel they belong to either community;. Based on these two dimensions, there are four modes of acculturation assimilation, separation, marginalisation and integration I will focus on integration, which occurs when there is involvement and participation with both the home culture and the wider receiving society Berry asserts that these modes, although experienced in slightly.
Democratic Punitive parenting 5 assimilation integration separation marginalisation participation 4 Time living in UK r = 467 r = 455 3 p. Acculturation process has many outcomes of which important ones are assimilation, rejection, integration, and marginalization The importance of acculturation can never be overemphasized in the study of cross cultural influences and the ways peoples of different ethnic identities learn to adapt and accept the cultural traits of a majority community in a multiethnic society. L'intégration se distingue de l'assimilation qui tend à faire disparaître toute spécificité culturelle La marginalisation est l'exclusion sociale d'une personne ou d'un groupe en raison d'un trop grand éloignement avec le mode de vie dominant dans la société.
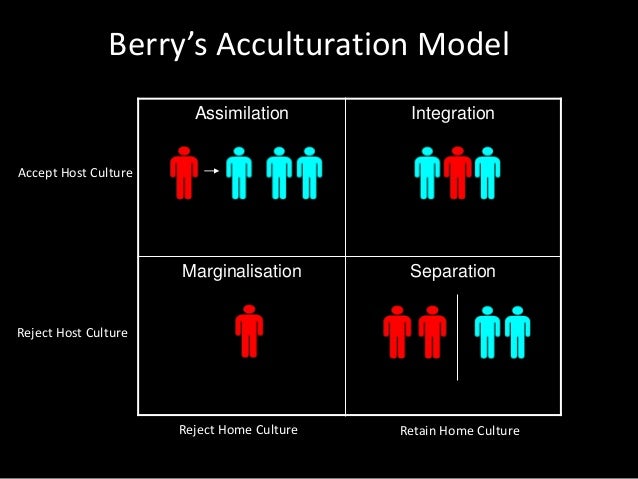
Of the host culture), assimilation (relinquish original culture, adopt the host culture), separation (maintain original culture and remain aloof from the host culture), and marginalisation (reject both the host culture and original culture) Previousresearchhasexploredattitudestowardsacculturation strategies and immigrants in general (Bourhis,. Acculturation attitudes integration, assimilation, separation, marginalisation Host group’s Acculturation Expectation A 16item scale assessing four acculturation expectation multiculturalism, melting pot, segregation, exclusion Immigrants’ Ethnic Identity A 7item scale assessing ethnic affirmation National Identity. That is the question which for centuries has confronted Jews living in the Diaspora.
η 2 = 03). One may speak of the separation or marginalization of immigrants, their adaptation, integration or assimilation into the majority environment In spite of the frequent use and intuitive understanding of those terms, there is no agreement as to their precise meanings. For behavioral shifts, the fewest behavioral changes result from the separation strategy, whereas most result from the assimilation strategy;.
The person undergoes integration, marginalisation, separation or assimilation The individual is said to undergo integration if he or she maintains their own cultural identity while participating in the host culture Marginalisation, on the other hand, will occur when an individual participates in neither his/her culture nor the host culture. Marginalisation involves two negative strategies, both towards native and towards hosting society, while assimilation involve one positive orientation towards host society and another negative towards newcomers Separation involve one positive strategy towards person’s native culture and negative relationship with host society. Berry’s Acculturation Model Assimilation Integration Marginalisation Separation Reject Home Culture Retain Home Culture Accept Host Culture Reject Host Culture 10 Berry’s Acculturation Model Assimilation Integration Marginalisation Separation Reject Home Culture Retain Home Culture Accept Host Culture Reject Host Culture 11.
Variations in ways of acculturating have become known by the terms integration, assimilation, separation, and marginalization Two variations in adaptation have been identified, involving. Integration involves the selective adoption of new behaviors from the larger society, and retention of valued features of one's heritage culture;. Assimilation You're willing to discard your culture of origin and fully identify with the new culture Separation You who hold on to your original culture at all cost and don't want to adopt the new culture Marginalization You don't identify with either your heritage culture or the new one, a rare situation.
Assimilation involves leaving behind the old culture Marginalization does this too, but without acceptance from the new culture Integration combines the old with the new culture. The segregation and assimilation policies additionally had an impact on the role models and roles within the Aboriginal family The policy of segregation impacted on the fathers position in the family, for as a result of the exploited labour, many fathers were unable to provide for their families, thus primary provider for the Aboriginal family came from the handouts given by the managers on the reserves. Assimilation or integration Similarities and differences between acculturation attitudes of migrants from Central Asia and Russians in Central Russia Established in 08, the Russian Psychological Society's Journal «Psychology in Russia State of the Art» publishes original articles.
SeparationThe individual maintains his or her own identity and does not absorbed into host culture IntegrationThe individual that maintains his own culture and also adapts the host culture MarginalizationThe individual does not identify with or participate in either his or her own culture or host culture Much crosscultural researched has focused on acculturation. Logic explains why assimilation = negative chauvinism = marginality, why measures of incompatible acculturative attitudes can be positively correlated, and why bicultural integration and. The results show evidence to support both the assimilation and integration hypotheses, but no evidence to support the separation or marginalisation hypotheses Based on the research findings, this study proposes the assimilation/integration pattern to summarise the urban integration pattern of migrant workers and argues that this pattern should be understood as being based on the social context of China.
Marginalization One fairly old and traditional way of looking at integration is Berry’s model of acculturation attitudes, where acculturation is seen as a process of moving from one stage to another In the universities, integration as a term is commonly used when speaking about international students. Strategies Integration, Assimilation, Separation, and Marginalisation (Berry, 1974) When there is an interest in maintaining one’s original cultural identity while remaining in daily interactions with other groups, Integration is the option When individuals do not wish to. Controversial London mayor Sadiq Khan recently toured the United States in support of presidential candidate Hillary Clinton Commenting on US immigration policy, Mr Khan said, “People shouldn’t have to drop their cultures and traditions when they arrive in our cities and countries”He also stated that he believes in “integration” rather than “assimilation”.
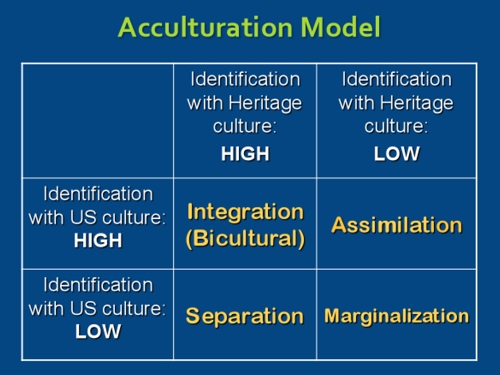
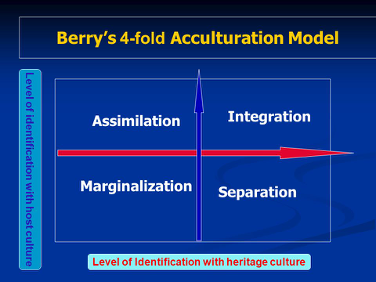
The selective adaptation of value systems, the processes of integration and differentiation, the generation of developmental sequences, and the operation of role determinants and personality factors (Social Science Research Council, 1954, p 974) According to this expanded view of acculturation, we see the inclusion of. Assimilation, integration, separation, and marginalization Berry (1997) proposes that individuals’ paths to assimilation vary on the basis of their level of identification with either the heritage or the US culture (see Figure 1) Figure 1 John Berry’s Acculturation Model According to Berry (1997), an individual. Marginalization Different acculturation strategies result in different mental health outcomes A common finding is that immigrants who integrate tend to have the best mental health,.
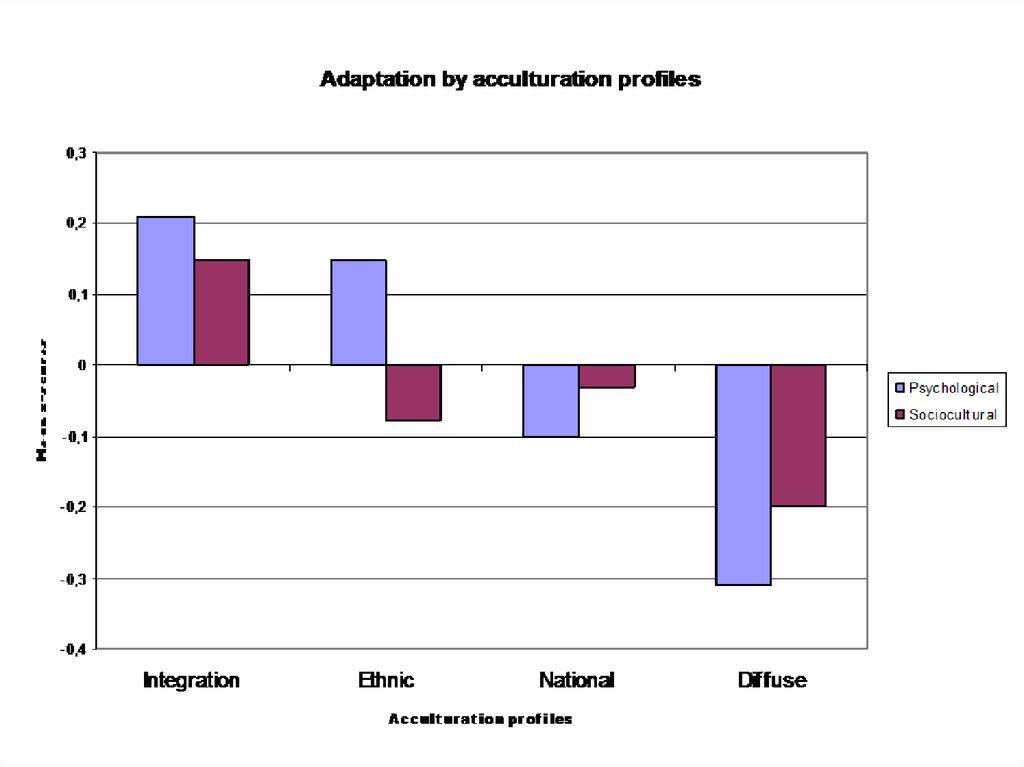
L’assimilation Pour un français né dans les années 1960, l’assimilation est longtemps allée de soi Pour un français né dans les années 1960, l’assimilation est longtemps allée de soi Dans la vie quotidienne, elle se traduisait par une discrétion de la part des immigrés, qui ne manifestaient pas en public leurs origines ethniques. Between integration, assimilation, separation and marginalisation academic editing Edyta Pindel This publication was carried out thanks to financing from the European Fund for the Integration of ThirdCountry Nationals as well as the national budget The sole responsibility for the content of this. These were an integration profile (364 % of immigrant youth), an ethnic or separation profile (225 %), a national or assimilation profile (187 %), and a diffuse or marginalisation profile (224 %) All adolescents for whom we had complete data (N = 4334) fit one of the four profiles The integration profile was the most frequent one It consisted of 1576 adolescents who indicated relatively high involvement in both their ethnic and national cultures.
From Assimilation to Integration from Separation to Marginalisation From Assimilation to Integration from Separation to Marginalisation The process of social, psychological, and cultural change and the risk factors for acculturative stress due to immigration. Integration was the acculturation style with the highest mean values, followed by assimilation and separation with similar mean scores The means for marginalization were the lowest The results of the MANOVA revealed a main effect for gender differences in acculturation style ( F (4, 433) = 379;. Furthermore, integration does not automatically guarantee the transition from segregation to inclusion According to the UN’s definitions, most of school districts in the United States are practicing integration rather than the “systematic reform” and “structural changes” that inclusion encompasses.
The process of acculturation can have four outcomes assimilation, integration, separation, and marginalization These four outcomes are shown in the picture to the right Assimilation is when one culture loses its original identity and takes on the identity of the other culture (in the picture, all of the blue dots become red dots). Adjusting to a new culture is challenging Berry's 4 acculturation strategies are assimilation, separation, marginalization and integration (bicultural). Controversial London mayor Sadiq Khan recently toured the United States in support of presidential candidate Hillary Clinton Commenting on US immigration policy, Mr Khan said, “People shouldn’t have to drop their cultures and traditions when they arrive in our cities and countries”He also stated that he believes in “integration” rather than “assimilation”.
Assimilation You're willing to discard your culture of origin and fully identify with the new culture Separation You who hold on to your original culture at all cost and don't want to adopt the new culture Marginalization You don't identify with either your heritage culture or the new one, a rare situation. Strategies (assimilation, integration, marginalisation, and separation) to explore the cultural identities of each participant By examining the acculturation model and determining which acculturation strategy participants have chosen, this will gather information about the how participants culturally adjust to US culture Finally, this. Marginalisation Often follows on enforced cultural loss, and is when individuals have no interest in integration or assimilation into the host culture, even though they have lost their own Application of this theory can be seen in the works of LyonsPadilla et al (15), who have developed a hypothesis that marginalisation in a globalised society leads to radicalisation.
Assimilation involves leaving behind the old culture Marginalization does this too, but without acceptance from the new culture Integration combines the old with the new culture. Assimilation You're willing to discard your culture of origin and fully identify with the new culture Separation You who hold on to your original culture at all cost and don't want to adopt the new culture Marginalization You don't identify with either your heritage culture or the new one, a rare situation. DOAJ is a communitycurated online directory that indexes and provides access to high quality, open access, peerreviewed journals.
– The purpose of this paper is to describe and analyse two features of multicultural societies diversity and equity The author argues that both these features are necessary for multicultural societies and their institutions to be successful Diversity is understood to include variations in culture, ethnicity, religion, age, gender and sexual orientation. Assimilation, marginalization, integration, and separation are the four main patterns of adaptation to a new culture Compared to optimists, pessimists are more likely to ignore problems Eustress is usually provoked by activities that are challenging, rewarding, and energizing. And marginalization is often associated with major heritage culture loss and the appearance of a number of dysfunctional and deviant behaviors (such as delinquency and substance and familial abuse).
Integration and maladaptation signifi cantly more negative than the corresponding correla tions for both assimilation and separation Fi nally, integration attitudes commonly accounted for 1% or. Integration When you hold on to some aspects of your own culture (cultural integrity) such as central norms and values, and at the same time, try to melt in to the new cultural environment Marginalization A strategy where you don’t keep hold on to your original culture, nor integrate in the new culture Isolation from both cultural groups!.
Files Eric Ed Gov Fulltext Ej Pdf
Repository Usfca Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 2235 Context Thes

Variants Of Biculturalism In Migrant And Host Adolescents Living In Italy And Spain Testing The Importance Of Life Domains Through The Relative Acculturation Extended Model Mancini 18 International Journal
Assimilation Integration Separation Marginalisation のギャラリー
Suvae S Adventure Pengpeng Yu
3

Pdf An Investigation Into The Acculturation Strategies Of Chinese Students In Germany Semantic Scholar
2
Download Atlantis Press Com Article Pdf
Define Acculturation Javatpoint

Economics Of International Migration10 Jan Brzozowski Phd Cracow University Of Economics Ppt Download
Web Uri Edu Iaics Files 15weihuayushuwang Pdf
Gale Academic Onefile Document L Acculturation Et La Migration Des Milleniaux Un Cadre De Congruence Culturelle

What Is Acculturation Ib Psychology

Contexts Ofacculturation Chapter 3 The Cambridge Handbook Of Acculturation Psychology

Acculturation Psychology Department Psychology Culture
2

Hispanic Acculturation Processes Evidence Against Assimilation Acr
Assimilation Or Integration Similarities And Differences Between Acculturation Attitudes Of Migrants From Central Asia And Russians In Central Russia Psychology In Russia State Of The Art

Course I Cross Cultural Psychology Intercultural Focus National Research
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf

Acculturation And Intergroup Communication Oxford Research Encyclopedia Of Communication
2

Acculturation Strategy And Racial Group In The Perception Of Immigrants

Social Capital Acculturation Attitudes And Sociocultural Adaptation Of Migrants From Central Asian Republics And South Korea In Russia Tatarko Asian Journal Of Social Psychology Wiley Online Library
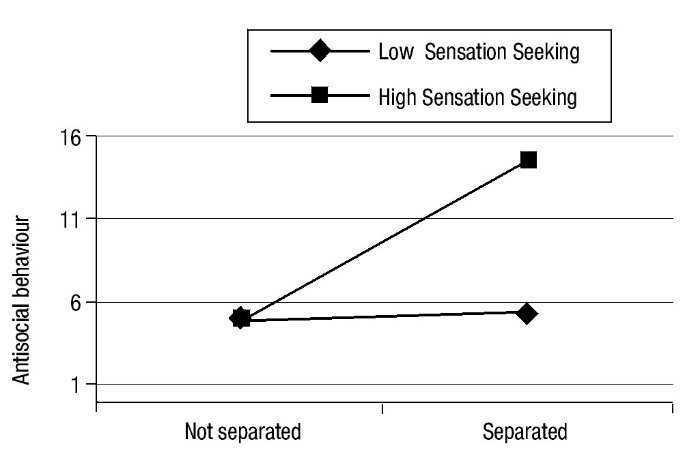
Interactive Effects Of Personality And Separation As Acculturation Style On Adolescent Antisocial Behaviour International Journal Of Clinical And Health Psychology
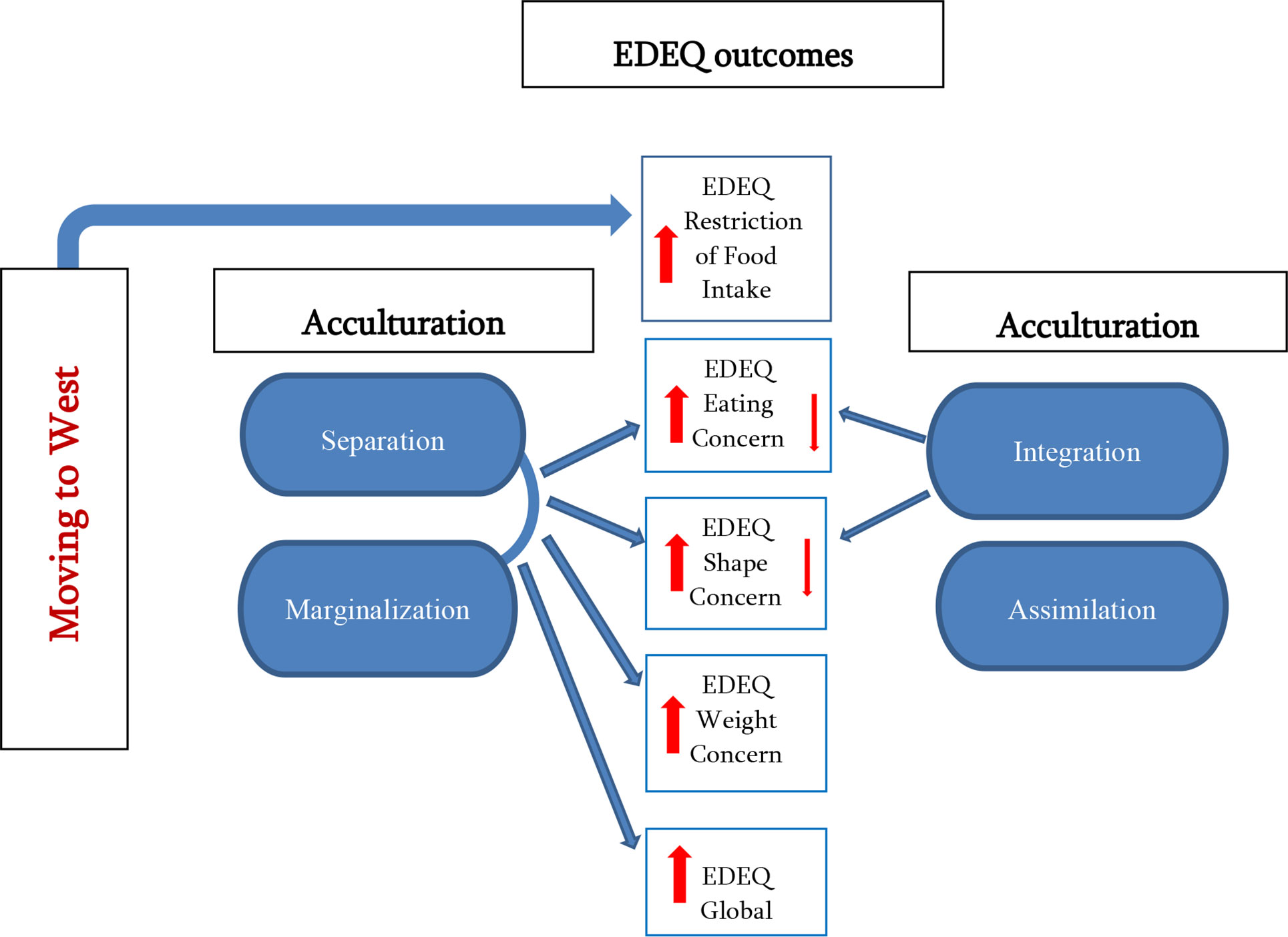
Frontiers Culture Change And Eating Patterns A Study Of Georgian Women Psychiatry
Http Institucional Us Es Revistas Estudios 18 2 L C3 pez rev Pdf

Greek Host Community Acculturation Expectations Towards Immigrants From Albania And Pakistan The Role Of Existential Parameters Tsouvelas The European Journal Of Counselling Psychology

The Moderating Role Of Acculturation Mode On The Relationship Between Depressive Symptoms And Health Related Quality Of Life Among International Students In Korea Archives Of Psychiatric Nursing
Repository Usfca Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 2235 Context Thes
Www Worldscientific Com Doi Pdf 10 1142 S
Multicultural

The Evaluation Of Immigrants Political Acculturation Strategies Sciencedirect
Integration Assimilation Or Separation The Implications For Marketers Of The Turkish Muslim Consumers In The Netherlands Emerald Insight

How Do International Students Acculturation Attitudes Affect Their Health Promoting Behaviors In Turkey In African And Asian Studies Volume 18 Issue 4 19

John W Berry Wikipedia
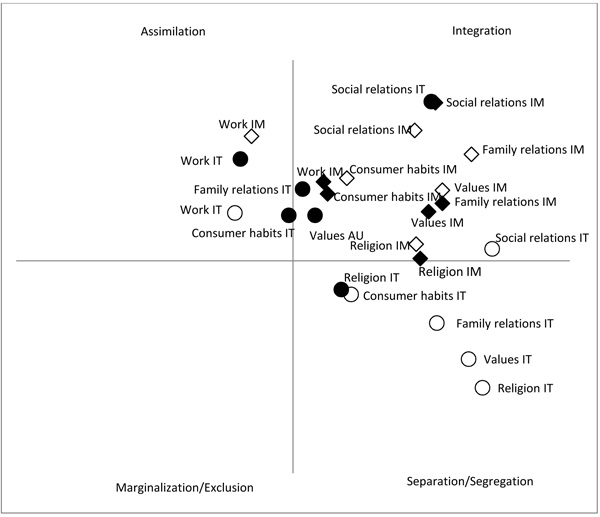
Acculturation Process And Life Domains Different Perceptions Of Native And Immigrant Adults In Italy Fulltext
Q Tbn And9gcszz0zmkuyiezsqsobzr Up1qq Nrt1scsrwuhq5f 0n78k11qg Usqp Cau

The Effects Of Perceived Islamophobia On Group Identification And Acculturation Attitudes Bastug 19 Canadian Review Of Sociology Revue Canadienne De Sociologie Wiley Online Library
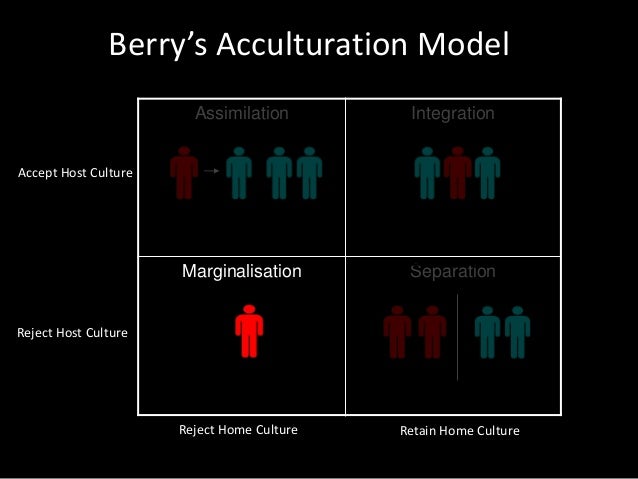
Understanding Cross Cultural Adjustment And Acculturation Theories

Different Types Of Acculturation Experience Integration Assimilation Download Scientific Diagram
Acculturation 4 Ways To Adjust To A New Culture Hoai Thu Truong

Acculturation Strategy And Racial Group In The Perception Of Immigrants

Figure 3
Www Jstor Org Stable

Cultural Adaptation Parenting And Child Mental Health Among English Speaking Asian American Immigrant Families Abstract Europe Pmc
Ethics And Skills For Psychologist As Supervisor Post Doctoral Super
Acculturation And Intercultural Psychology Online Presentation
Sociocultural Models Of Second Language Learning Of Young Immigrants In Canada Intechopen
2
Http Www Reading Ac Uk Nmsruntime Saveasdialog Aspx Lid Sid
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf
Acculturation

Acculturation Strategy And Racial Group In The Perception Of Immigrants

The Process Of Acculturation And The Role Of Festivals Immifest
Web Uri Edu Iaics Files 04 Ngwira Mapoma Hong Sariyo Kondowe Pdf
Http Zeynepaycan Net Doc J27 Pdf
Http Www Migracje Civitas Edu Pl Migracje Images Pdf Eng Chapter 3 Pdf

What Is Integration And Why Is It Important For Internationalisation A Multidisciplinary Review

Opinion Are You Confused About Integration And Assimilation Integracija
Acculturation And Intercultural Psychology Online Presentation

Pdf Acculturation Strategies And Attitudes Of African Immigrants In The South Of Spain Between Reality And Hope
2

Tourists Strategies An Acculturation Approach Sciencedirect
Arxiv Org Pdf 1810
2

Influence Of Acculturation Strategies On The Judgment Of A Violent Act Committed By A North African Woman
Berry S Model Of Acculturation Working In A Cross Cultural Team Berry S Model Of Acculturation
Orientaciones De Aculturacion Estres De Aculturacion Y Bienestar Psicologico En Inmigrantes Latinoamericanos En Santiago De Chile
Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 16
Www Econstor Eu Bitstream 1724 1 Abl Argomenti 17dec Pdf
1 7 Intercultural Communication Competence Social Sci Libretexts
Are Americans More Successful At Building Intercultural Relations Than Japanese A Comparison And Analysis Of Acculturation Outcomes In Japan Springerplus Full Text
Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1037 10 2680 7 1 3
Workshop Acculturation Cfc
1
Are Americans More Successful At Building Intercultural Relations Than Japanese A Comparison And Analysis Of Acculturation Outcomes In Japan Springerplus Full Text
2

The Formulation Of Acculturation Strategies In A Multicultural Society Download Scientific Diagram
Chapter 12 The Potential For Intercultural Competence Intercultural Competence Research Project South Korea

Cross Cultural Ch 7 Flashcards Quizlet

Exploring Migrant Families Acculturation And Livelihoods In Canada And The Role Of Sport Participation Journal Of Sport For Development

Cfs 4 Midterm Diagram Quizlet
Understanding Cross Cultural Adjustment And Acculturation Theories

Ethics Is More Than A Code

Acculturation Wikipedia
3
Scholarworks Gvsu Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 1275 Context Iaccp Papers
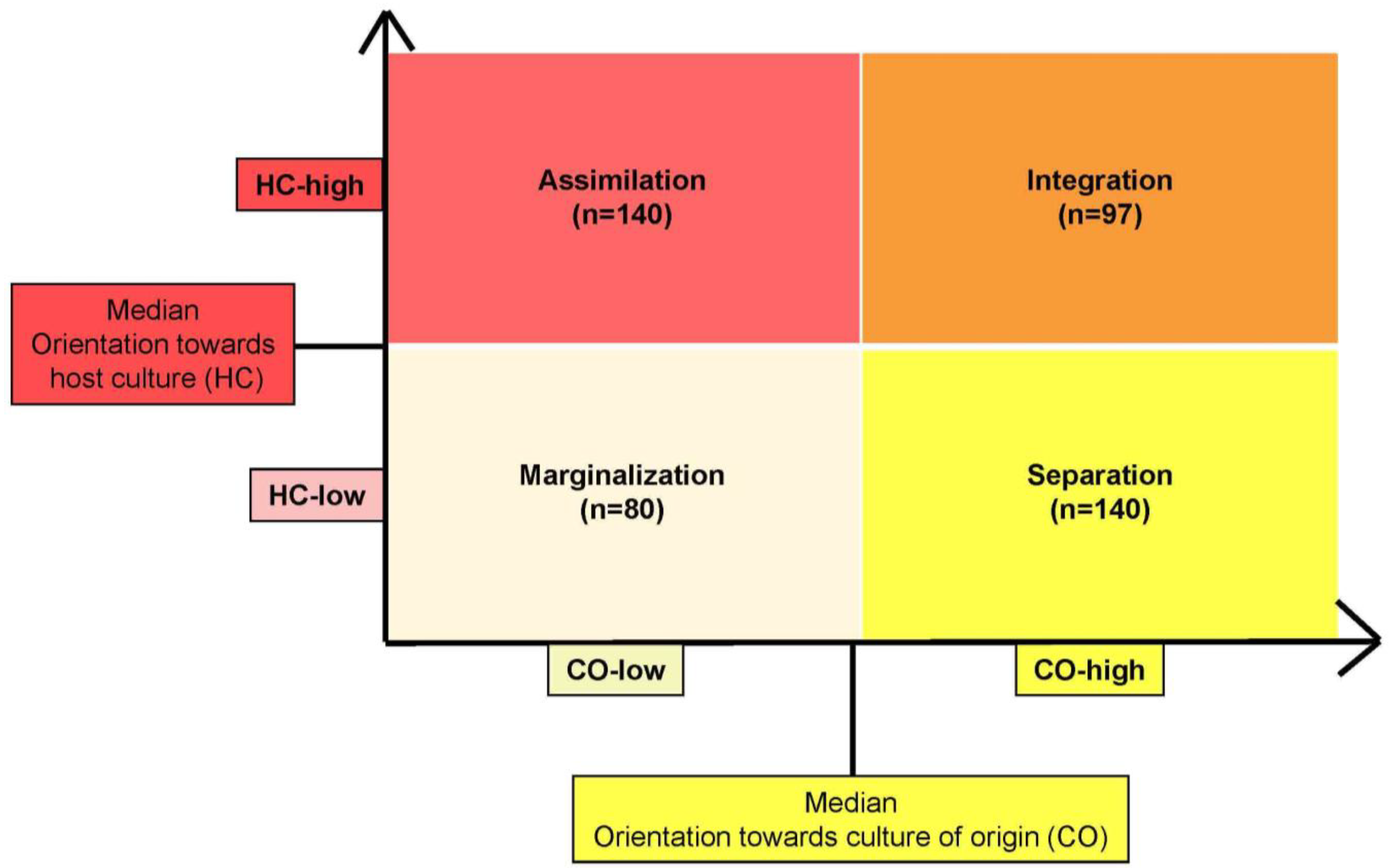
Ijerph Free Full Text Acculturation And Depressive Symptoms Among Turkish Immigrants In Germany Html

Xixth International Congress Of The International Association For Cross Cultural Psychology July 27 31 08 Bremen Germany Chirkov Boski Symposium Ppt Download

Integrating Translucent Acculturation By Alex Michael Fogleman Medium
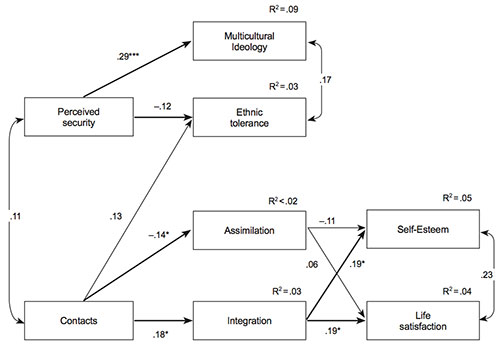
Assimilation Or Integration Similarities And Differences Between Acculturation Attitudes Of Migrants From Central Asia And Russians In Central Russia Psychology In Russia State Of The Art

Domains Of Identity Adolescent Psychology

Ppt Cross Cultural Adjustment Emotional Well Being Powerpoint Presentation Id

Four Acculturation Strategies Berry 1997 01 Download Scientific Diagram
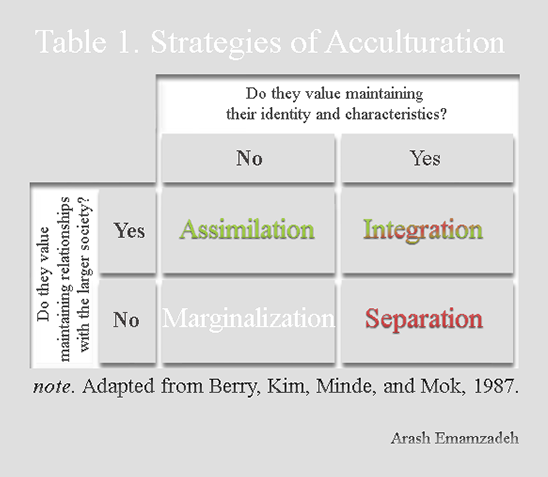
Acculturation And Migration Interview With Dr J W Berry Psychology Today
Towards A Framework For Understanding Ethnic Consumers Acculturation Strategies In A Multicultural Environment A Food Consumption Perspective Emerald Insight
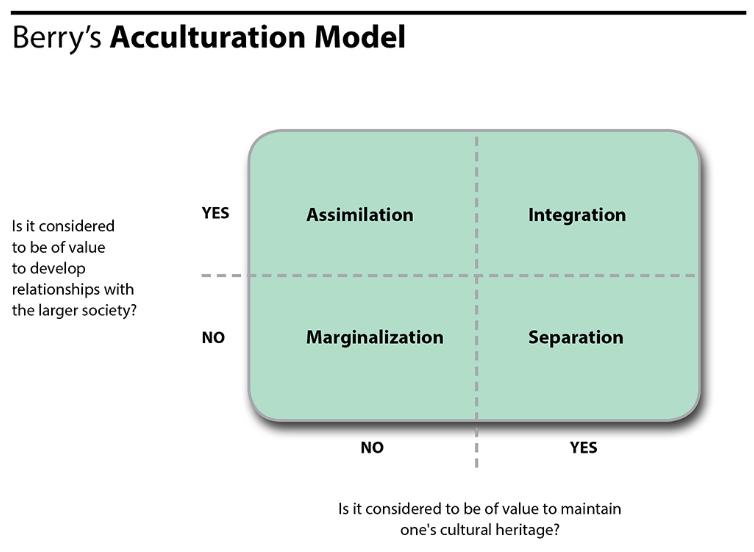
Culture Acculturation

Pdf The Interplay Of International Students Acculturative Stress Social Support And Acculturation Modes Semantic Scholar
Navigating Cultural Spaces A Transactional Perspective On Immigration Springerlink

Acculturation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Acculturation Orientations Affect The Evolution Of A Multicultural Society Nature Communications
Ormer Sakarya Edu Tr Uploads Files Asylum Seekers Experience And Acculturation A Study Of Syrian University Students In Turkey Pdf

Key Studies Effects Of Acculturation On Behaviour Torres Et Al 12 And Nap Et Al 14 Ib Psychology




