Integration Assimilation Separation And Marginalization
‘assimilation,’ ‘separation,’ ‘marginalization,’ and ‘integration’ The individual’s chosen strategy will be determined by (1) a preference for the majority or for the heritage culture and (2) a preference for having contact with and participating in society with other cultural groups (Berry 1980) Assimilation generally still.

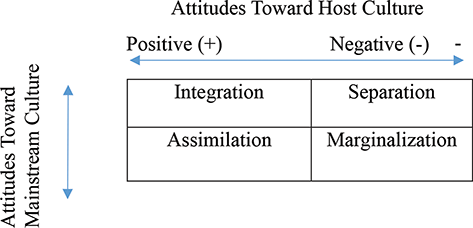
Integration assimilation separation and marginalization. Separation (marginalization) Adaptation Integration Assimilation Source Own work The four dimensions of an immigrant’s “entry” into the host society Speaking of the adaptation, integration or assimilation of immigrants into the host community, we should distinguish four dimensions of these. OK, it is perfect time to mix up reallife and studies!. Attitudes or orientation towards one's heritage culture and new culture;.
The authors examined the extent to which Berry's (1997) acculturation orientation categoriesassimilation, integration, separation, and marginalizationwould emerge from a latent class analysis of continuous acculturation indices Hispanic college students (N = 436) from Miami participated in the study. Strategies assimilation, separation, marginalization, or integration Assimilation occurs when individuals prefer interaction in the new culture and wish to distance themselves from their origin culture Alternatively, separation happens when individuals chose their origin culture and avoid interaction with the new culture When an individual. Second, some studies mix different levels of analysis with respect to culture constructs, eg national vs organizational culture;.
However, her classmates tend to reject her because of her accent and their prejudice toward her country of origin. M BudytaBudzyńska Published11 Immigrants find their place in the host society in a variety of ways and, therefore, various different terms are used to describe the degree in which they “enter” into the host community, both in everyday usage and in scholarly analyses One may speak of the separation or marginalization of immigrants, their adaptation, integration or assimilation into the majority environment. Using data from an international collaborative research project on youth resilience in the context of migration, this study aims to investigate how different acculturation patterns (ie integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization) influence the mental health of migrant youth, and whether resilience might function as a mediator in the association between acculturation and mental health.
Integration assimilation, separation marginalization ASSIMILATION a group does not maintain its cultural distinctiveness and moves increasingly toward participation with the larger society. Integration, Separation, and Marginalization on a fourpoint scale The results suggested that Integration was the most preferred strategy while Marginalization was the least preferred strategy in both years of the study Moreover, Latvian language knowledge and use was positively correlated with Assimilation and Integration. Critical history of the acculturation psychology of assimilation, separation, integration, and marginalization March 03 Review of General Psychology 7(1)337.
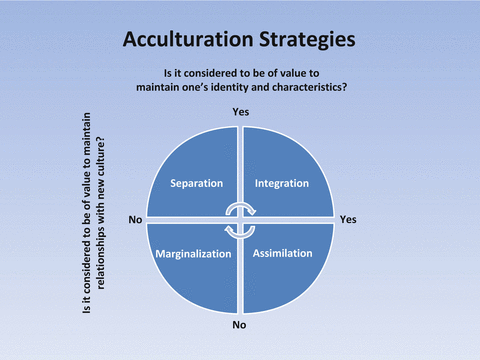
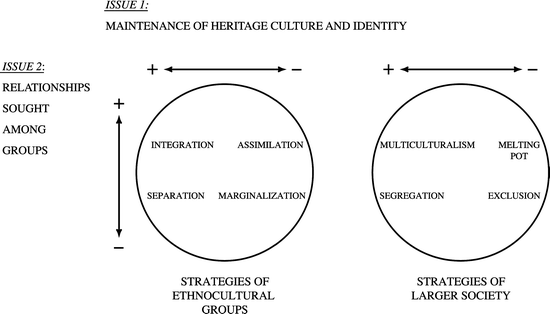
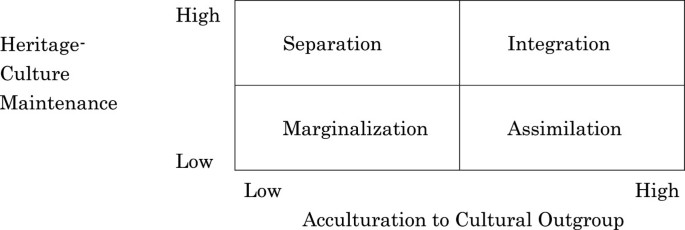
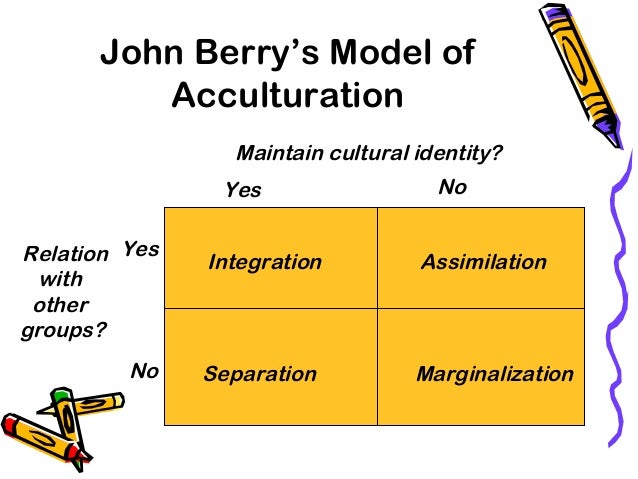
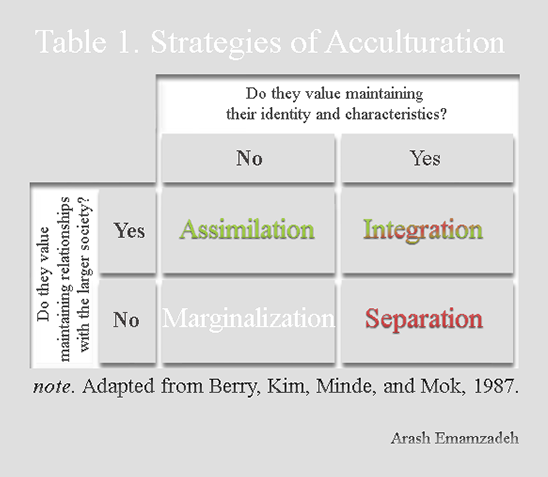
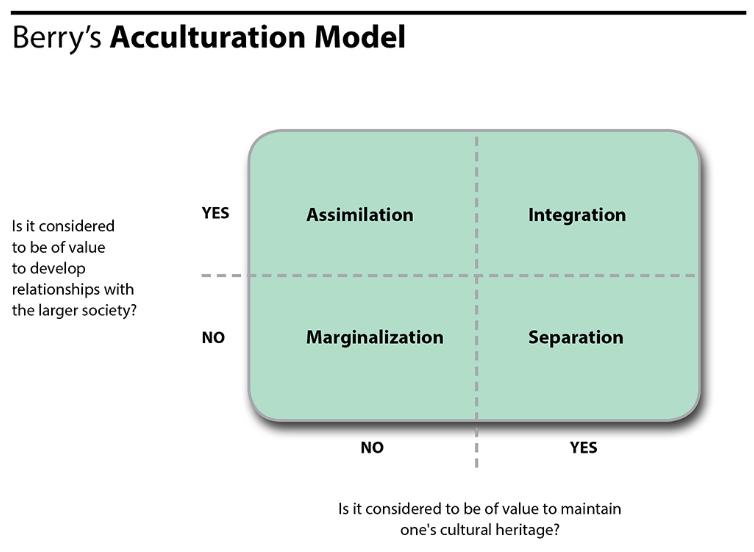
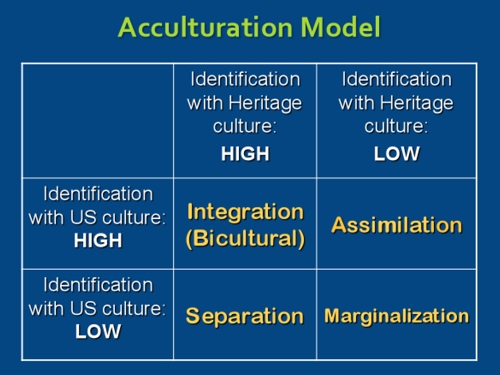
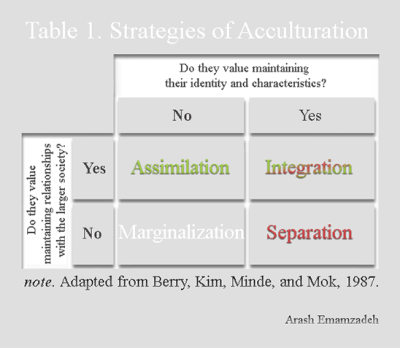
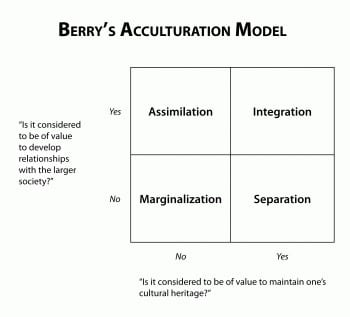
Include multiculturalism (integration), melting pot (assimilation), segregation (separa tion), and exclusion (marginalization) (Berry, 01) Several studies reveal the receiving society’s preference for assimilation (Van Ouden hoven, Prins, & Buunk, 1998). SeparationThe individual maintains his or her own identity and does not absorbed into host culture IntegrationThe individual that maintains his own culture and also adapts the host culture MarginalizationThe individual does not identify with or participate in either his or her own culture or host culture Much crosscultural researched has focused on acculturation. The model proposed by Berry includes four quadrants, namely assimilation, integration, separation, and marginalization Berry (1997) proposes that individuals’ paths to assimilation vary on the basis of their level of identification with either the heritage or the US culture (see Figure 1) Figure 1 John Berry’s Acculturation Model.
‘assimilation,’ ‘separation,’ ‘marginalization,’ and ‘integration’ The individual’s chosen strategy will be determined by (1) a preference for the majority or for the heritage culture and (2) a preference for having contact with and participating in society with other cultural groups (Berry 1980) Assimilation generally still. Accordingly, it can be assumed that people with an integration or assimilation attitude will accept contact or interact directly with members of the outgroup while people with a separation or marginalization attitude will avoid direct interaction A variable that could help to create a favourable condition is selfe†cacy. Marginalization Integration is when individuals maintain their cultures and are able to accept and adapt to the host’s cultures In contrast, assimilation is when individuals fully adapt to the host’s cultures, while they become more alienated toward their own cultures On the other hand, separation is when individuals become alienated toward the host culture and separate themselves from the main society.
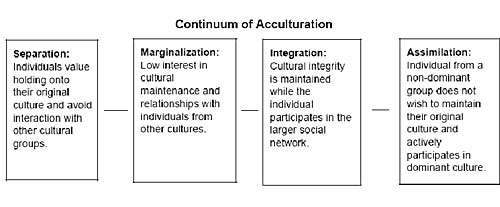
Each acculturation style (assimilation, integration, separation and marginalization) was assessed with three items each covering language use, social contacts, values and attitudes Participants rated the items on a Likertscale ranging from 1 = “not at all true” to 4 = “totally true”. Integration is a process where the minority cultures take something in from the majority culture to become a part of the majority culture retaining their identity Assimilation Assimilation is a process of absorbing minority communities into the ways and views of the majority community in a multicultural society. Integration occurs when individuals are able to adopt the cultural norms of the dominant or host culture while maintaining their culture of origin Integration leads to, and is often synonymous with biculturalism Marginalization occurs when individuals reject both their culture of origin and the dominant host culture.
Integration is a process where the minority cultures take something in from the majority culture to become a part of the majority culture retaining their identity Assimilation Assimilation is a process of absorbing minority communities into the ways and views of the majority community in a multicultural society. Consequently, integration occurs when both cultural maintenance and contact are successfully negotiated Those pursuing assimilation experience a high level of cultural contact, while separation supports cultural maintenance among immigrant groups Finally, marginalization undervalues one’s cultural identity and contact with others. The authors examined the extent to which Berry's (1997) acculturation orientation categoriesassimilation, integration, separation, and marginalizationwould emerge from a latent class analysis of continuous acculturation indices Hispanic college students (N = 436) from Miami participated in the study.
Separation was associated with poorer physical and mental health (linear regression coefficient (RC) = 23, 95% CI 39 to 08 and RC = 24, 95% CI 44 to 05, respectively;. Adjusting to a new culture is challenging Berry's 4 acculturation strategies are assimilation, separation, marginalization and integration (bicultural). Integration leads to, and is often synonymous with biculturalism Marginalization – Marginalization occurs when individuals reject both their culture of origin and the dominant host culture Predictors of Acculturation Strategies edit edit source.
The EAAM was developed to categorize acculturating individuals into one of Berry’s (1980) four categories Assimilation, Integration, Separation and Marginalization, as shown in Table 1 Items were changed from referring specifically to Asian students to refer to international students in general. First, we hypothesized that latent class analysis would identify four subgroups of South Asian immigrants characterized by distinctive patterns of cultural attitudes and behaviors, corresponding to the integration, assimilation, separation, and marginalization strategies described by Berry Next, we hypothesized that younger respondents, men, the unmarried, those with no religious affiliation, those with higher levels of education, the currently employed, those with greater per capita. Critical History of the Acculturation Psychology of Assimilation, Separation, Integration, and Marginalization Floyd W Rudmin Review of General Psychology 03 7 1 , 337.
Acculturation process has many outcomes of which important ones are assimilation, rejection, integration, and marginalization The importance of acculturation can never be overemphasized in the study of cross cultural influences and the ways peoples of different ethnic identities learn to adapt and accept the cultural traits of a majority community in a multiethnic society. When the process is at its most extreme, assimilation occurs wherein the original culture is wholly abandoned and the new culture adopted in its place However, other outcomes can also occur that fall along a spectrum from minor change to total change, and these include separation, integration, marginalization, and transmutation. Assimilation 2 Separation 3 Integration 4 Marginalization STUDY 2 Semistructural interviews • The evaluations of the qualitative data (semistructural interviews with host culture members and immigrants) OBJECTIVES.
Individuals and populations assimilation, integration, separation, and marginalization Berry’s model for exploring the acculturative process has been widely used in research spanning multiple academic disciplines, and has provided a fundamental theoretical framework for the study of acculturation psychology (Sullivan & KashubeckWest, 15;. And finally, there exist various definitions of “M&A success”, which become. Culture and identity and attitude towards learning and interacting with new culture T he model shows that integration exposes positive relationship with both cultures, while marginalization shows negative attitude to both cultures Separation occurs when only the home culture is maintained, and the attachment with the host culture is totally ignored.
Integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization The table below demonstrates Berry‟s model of acculturation through a biodimensional framework Table 1 Acculturation Framework Attitude towards keeping Heritage culture and identity Attitude towards learning and interacting with new culture Positive Negative. Acculturation process has many outcomes of which important ones are assimilation, rejection, integration, and marginalization The importance of acculturation can never be overemphasized in the study of cross cultural influences and the ways peoples of different ethnic identities learn to adapt and accept the cultural traits of a majority. Separation involves identification with only the culture of one’s heritage country and contacts with one’s own group members Assimilation involves identification with the host country’s culture and nonacceptance of one’s heritage culture Marginalization is the absence of identification with both cultures.
Sixteen possibilities (4 x 4) were generated from the four stages of a sexualdevelopment model (Initiation, Primacy, Conflict, and Identity synthesis) and the four strategies of J W Berry's (1980) acculturation model (Assimilation, Integration, Separation, and Marginalization). The process of interaction and integration among people of dif Enculturation refers to the process by which young people lear Integration, assimilation, separation, and marginalization. Controversial London mayor Sadiq Khan recently toured the United States in support of presidential candidate Hillary Clinton Commenting on US immigration policy, Mr Khan said, “People shouldn’t have to drop their cultures and traditions when they arrive in our cities and countries”He also stated that he believes in “integration” rather than “assimilation”.
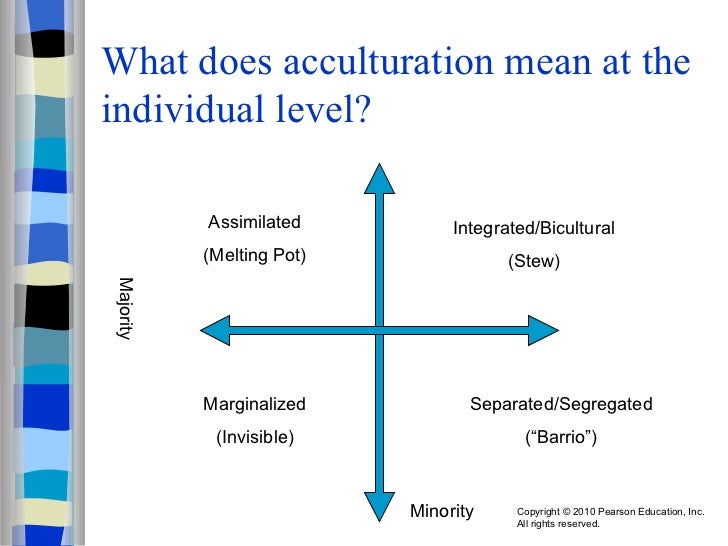
Assimilation You're willing to discard your culture of origin and fully identify with the new culture Separation You who hold on to your original culture at all cost and don't want to adopt the new culture Marginalization You don't identify with either your heritage culture or the new one, a rare situation. Marginalization Integration is when individuals maintain their cultures and are able to accept and adapt to the host’s cultures In contrast, assimilation is when individuals fully adapt to the host’s cultures, while they become more alienated toward their own cultures On the other hand, separation is when individuals become alienated toward the host culture and separate themselves from the main society. The separation strategy is used when individuals maintain their heritage.
Acculturation (eg, Integration, Assimilation, Separation, and Marginalization) and subjective wellbeing (SWB) among Asian Indians residing in the United States Few studies have examined this relationship among Asian Indians residing in the United States Participants were 255 firstand secondgeneration Asian Indians in the United States from. Assimilation You're willing to discard your culture of origin and fully identify with the new culture Separation You who hold on to your original culture at all cost and don't want to adopt the new culture Marginalization You don't identify with either your heritage culture or the new one, a rare situation. Assimilation involves leaving behind the old culture Marginalization does this too, but without acceptance from the new culture Integration combines the old with the new culture.
Assimilation Separation Integration Marginalization When you abandon your own cultural habits and values in order to accept the new country totally Isolation from both cultural groups!. Defines separation, and the reverse defines assimilation The model highlights the fact that acculturation proceeds in diverse ways and that it is not necessary for immigrants to give up their culture of origin in order to adapt to the new society This approach suggests that earlier models recognizing only assimilation or marginalization (eg, Stonequist, 1935) are too limited Most importantly, the. In the study sample, 75% are in the integration group, 15% in assimilation, 6% in separation, and 5% in marginalization Wellbeing is assessed with two questions about life satisfaction and selfrated mental health Those in the integration group have a significantly higher level on both measures of wellbeing.
Sam & Berry, 1995 as cited in Farver et al, 02) assessed the acculturation strategies of various immigrant groups in North America and the result showed that integration was the most psychologically adaptive attitude, arguing that integrated or bicultural individuals experienced less acculturative stress and anxiety and manifested fewer psychological problems than those who were marginalized, separated, or assimilated, whereas marginalized individuals suffered the most psychological. Consequently, integration occurs when both cultural maintenance and contact are successfully negotiated Those pursuing assimilation experience a high level of cultural contact, while separation supports cultural maintenance among immigrant groups Finally, marginalization undervalues one’s cultural identity and contact with others. M BudytaBudzyńska Published11 Immigrants find their place in the host society in a variety of ways and, therefore, various different terms are used to describe the degree in which they “enter” into the host community, both in everyday usage and in scholarly analyses One may speak of the separation or marginalization of immigrants, their adaptation, integration or assimilation into the majority environment.
The assimilation strategy is used when immigrants reject their heritage culture but embrace the host culture;. Integration, Separation, and Marginalization on a fourpoint scale The results suggested that Integration was the most preferred strategy while Marginalization was the least preferred strategy in both years of the study Moreover, Latvian language knowledge and use was positively correlated with Assimilation and Integration. In the study sample, 75% are in the integration group, 15% in assimilation, 6% in separation, and 5% in marginalization Wellbeing is assessed with two questions about life satisfaction and selfrated mental health Those in the integration group have a significantly higher level on both measures of wellbeing.
Marginalization and separation are associated with high levels of acculturative stress (as assessed by the measurement of psychological and psychosomatic symptoms), integration is associated with a low level of stress, and assimilation is linked with an intermediate stress level (Berry et al, 1987). The analyzed articles reveal three major reasons for the inconsistent findings in M&A research first, most scholars refer to “integration” as an umbrella term for different and distinctive acculturation strategies, eg integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization;. In general, integration has been found to be the most preferred strategy among immigrants, followed by separation and assimilation, and marginalization is the least frequent Integration is also argued to be the most adaptive pathway because it implies bicultural competence and flexibility.
The concept of acculturation strategies refers to some different ways for how groups and individuals seek to live together, using the four concepts of integration (engaging both cultures), assimilation or separation (engaging only one or the other culture) and marginalisation (engaging neither culture). Integration, assimilation, separation, marginalization Integration () attitude towards keeping heritage culture and identity. Furthermore, integration does not automatically guarantee the transition from segregation to inclusion According to the UN’s definitions, most of school districts in the United States are practicing integration rather than the “systematic reform” and “structural changes” that inclusion encompasses.
Integration Separation Marginalization Assimilation High Latino Acculturation High Anglo Acculturation High Latino Acculturation Low Anglo Acculturation Low Latino Acculturation High Anglo Acculturation Low Latino Acculturation Low Anglo Acculturation Berry’s Multidimensional Model and Marin & Gamba, 1996 Bidimensional Acculturation Scale 1. Reference integration) Marginalization was associated with poorer mental health in descendants of migrants (RC = 64, 95% CI 1 to 08;. According to Berry (1997), four acculturation strategies were introduced assimilation, separation, marginalization, and integration When individuals do not wish to maintain their cultural identity and seek daily interaction with other new cultures, the assimilation strategy is defined.
High Add Question Here Question 248 Multiple Choice 0 points Modify Remove Question After coming to the US, Asma learned English quickly and wanted to completely immerse herself in the American culture;. This study was guided by Berry’s acculturation framework, which hypothesizes the existence of four acculturation strategies integration, assimilation, separation, and marginalization The integration strategy is used when individuals maintain their heritage culture and adopt elements of the host culture;. Assimilation involves leaving behind the old culture Marginalization does this too, but without acceptance from the new culture Integration combines the old with the new culture.
Assimilation You're willing to discard your culture of origin and fully identify with the new culture Separation You who hold on to your original culture at all cost and don't want to adopt the new culture Marginalization You don't identify with either your heritage culture or the new one, a rare situation.

Four Acculturation Strategies Berry 1997 01 Download Scientific Diagram
Immigration Acculturation And Drug Use Springerlink

Pdf Critical History Of The Acculturation Psychology Of Assimilation Separation Integration And Marginalization Semantic Scholar
Integration Assimilation Separation And Marginalization のギャラリー
Multicultural
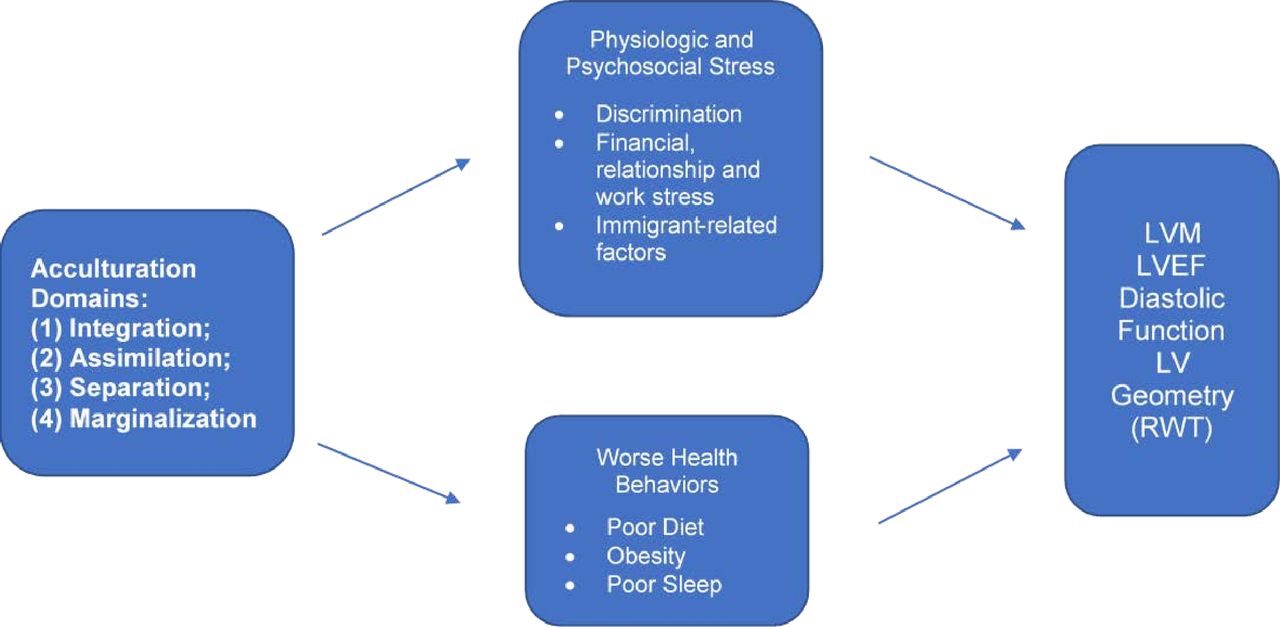
Association Of Acculturation With Cardiac Structure And Function Among Hispanics Latinos A Cross Sectional Analysis Of The Echocardiographic Study Of Latinos Bmj Open

Pdf Acculturation Strategies And Attitudes Of African Immigrants In The South Of Spain Between Reality And Hope

Migrant Host Relationships Ppt Download

Student Activity 6 Examining How Other Cultures Conform To Their Host Culture Studocu

John W Berry Wikipedia
Ethics And Skills For Psychologist As Supervisor Post Doctoral Super

Economics Of International Migration10 Jan Brzozowski Phd Cracow University Of Economics Ppt Download

Sage Reference The Sage Handbook Of Applied Social Psychology

Integrating Translucent Acculturation By Alex Michael Fogleman Medium
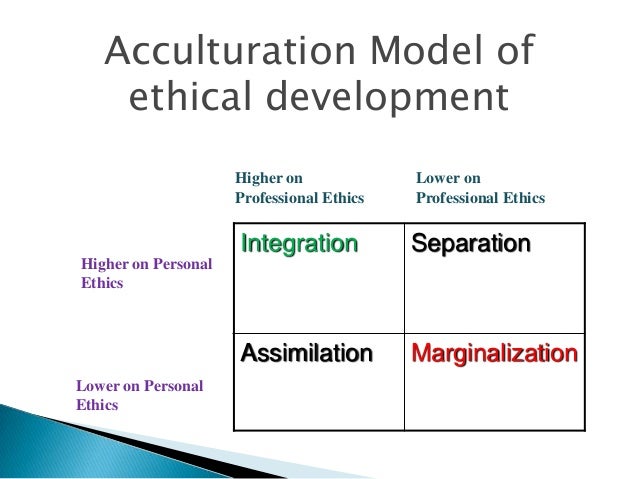
Ethical Decision Making Part 2

Solved Incorrect Question 1 0 1 Pts Which Of The Followin Chegg Com

Psychology 307 Cultural Psychology Ppt Video Online Download

Exploring Migrant Families Acculturation And Livelihoods In Canada And The Role Of Sport Participation Journal Of Sport For Development

The Influence Of Culture Of Honor And Emotional Intelligence In The Acculturation Of Moroccan Immigrant Women Semantic Scholar

The Effects Of Perceived Islamophobia On Group Identification And Acculturation Attitudes Bastug 19 Canadian Review Of Sociology Revue Canadienne De Sociologie Wiley Online Library
Frontiers Culture Change And Eating Patterns A Study Of Georgian Women Psychiatry

Migrant Host Relationships Ppt Download
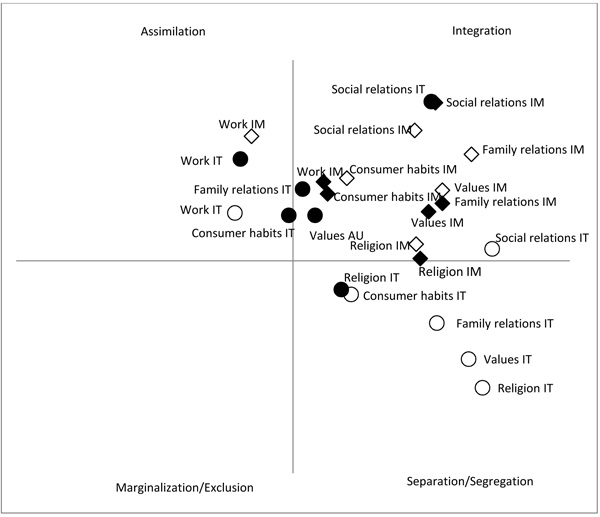
Acculturation Process And Life Domains Different Perceptions Of Native And Immigrant Adults In Italy Fulltext

Domains Of Identity Adolescent Psychology
Mobility And Acculturation Springerlink

Acculturation Wikipedia
Are Americans More Successful At Building Intercultural Relations Than Japanese A Comparison And Analysis Of Acculturation Outcomes In Japan Springerplus Full Text

Acculturation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ppt Race And Ethnic Variations
Workshop Acculturation Cfc

Pdf Acculturation Strategy Of Alor Community In Java

How Do International Students Acculturation Attitudes Affect Their Health Promoting Behaviors In Turkey In African And Asian Studies Volume 18 Issue 4 19
Orientaciones De Aculturacion Estres De Aculturacion Y Bienestar Psicologico En Inmigrantes Latinoamericanos En Santiago De Chile
Acculturation And Migration Interview With Dr J W Berry Psychology Today
Sociocultural Models Of Second Language Learning Of Young Immigrants In Canada Intechopen

Interactive Theory Of Acculturation Bourhis Major Reference Works Wiley Online Library

Cross Cultural Ch 7 Flashcards Quizlet

Pdf The Interplay Of International Students Acculturative Stress Social Support And Acculturation Modes Semantic Scholar

Social Capital Acculturation Attitudes And Sociocultural Adaptation Of Migrants From Central Asian Republics And South Korea In Russia Tatarko Asian Journal Of Social Psychology Wiley Online Library

Pdf Language Learners Acculturation Attitudes
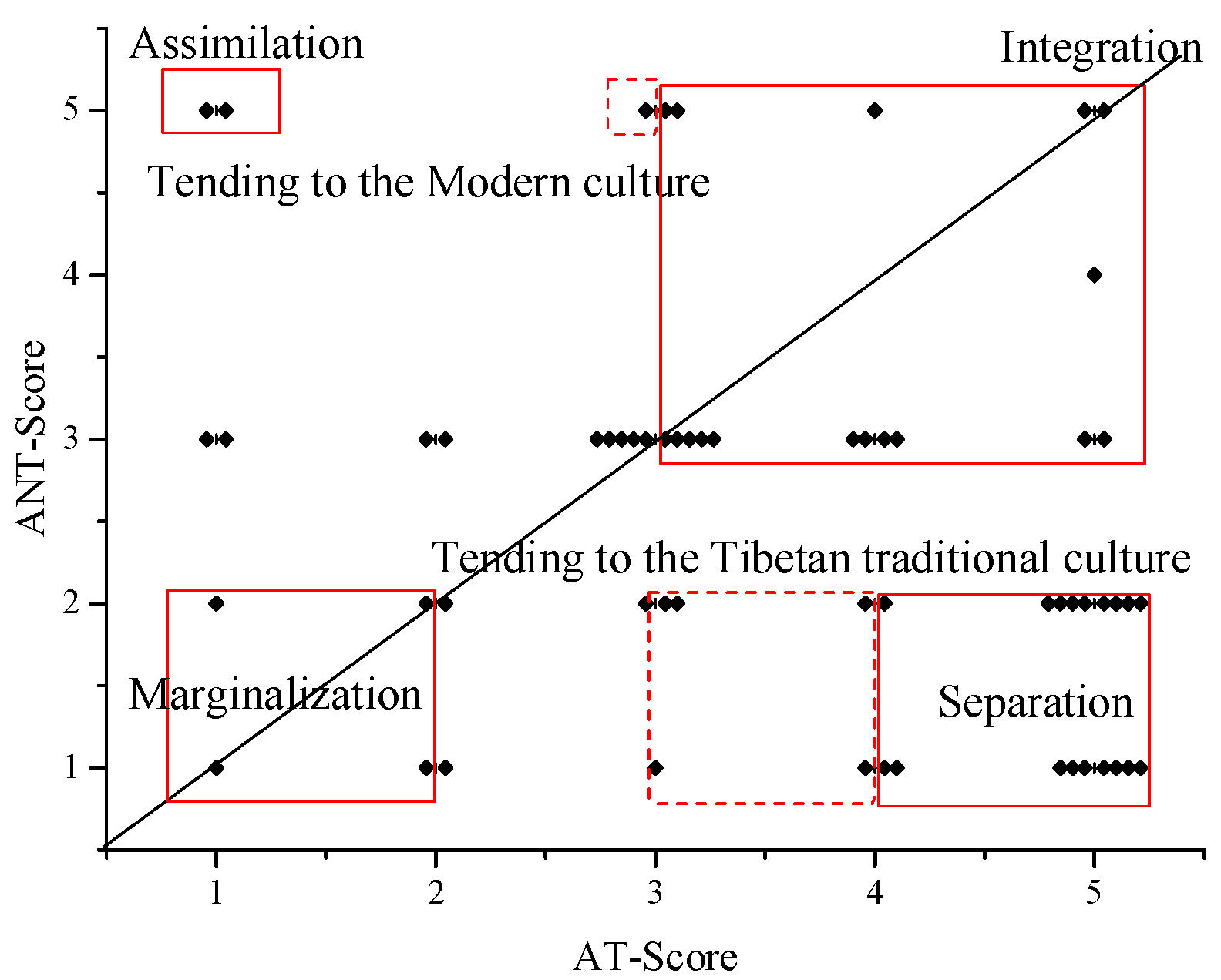
Sustainability Free Full Text Research On Tibetan Folk S Contemporary Tibetan Cultural Adaptive Differences And Its Influencing Factors Taking Shigatsecity Tibet China As An Example Html
Culture Acculturation
Acculturation 4 Ways To Adjust To A New Culture Hoai Thu Truong

The Moderating Role Of Acculturation Mode On The Relationship Between Depressive Symptoms And Health Related Quality Of Life Among International Students In Korea Archives Of Psychiatric Nursing
Acculturation
Do Acculturation Strategies Have Impacts On The Self Declared Health Well Being And Lifestyle Of First Generation Allophone Immigrants In Montreal Canada Emerald Insight

Different Types Of Acculturation Experience Integration Assimilation Download Scientific Diagram
Berry S Model Of Acculturation Working In A Cross Cultural Team Berry S Model Of Acculturation
Acculturation Economic Stress Social Relationships And School Satisfaction Among Migrant Children In Urban China Springerlink
Are Americans More Successful At Building Intercultural Relations Than Japanese A Comparison And Analysis Of Acculturation Outcomes In Japan Springerplus Full Text

Key Studies Effects Of Acculturation On Behaviour Torres Et Al 12 And Nap Et Al 14 Ib Psychology

The Evaluation Of Immigrants Political Acculturation Strategies Sciencedirect
Acculturation And Intercultural Psychology Online Presentation

The Formulation Of Acculturation Strategies In A Multicultural Society Download Scientific Diagram

Ppt Cross Cultural Adjustment Emotional Well Being Powerpoint Presentation Id

A Critique Of Critical Acculturation Sciencedirect
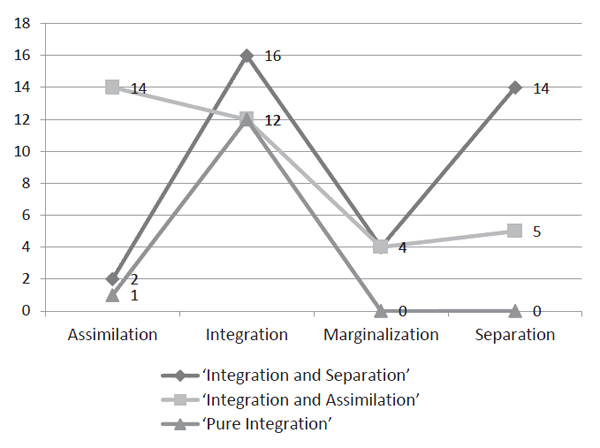
Value Shifts In Vietnamese Students Studying In Russia Psychology In Russia State Of The Art
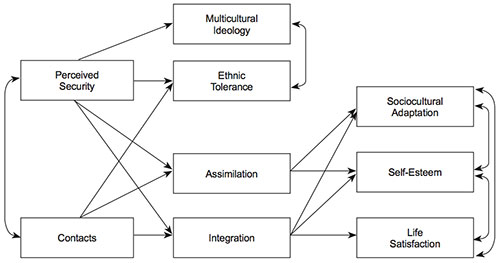
Assimilation Or Integration Similarities And Differences Between Acculturation Attitudes Of Migrants From Central Asia And Russians In Central Russia Psychology In Russia State Of The Art

Influence Of Acculturation Strategies On The Judgment Of A Violent Act Committed By A North African Woman

Ethics Is More Than A Code

Acculturation And Intergroup Communication Oxford Research Encyclopedia Of Communication
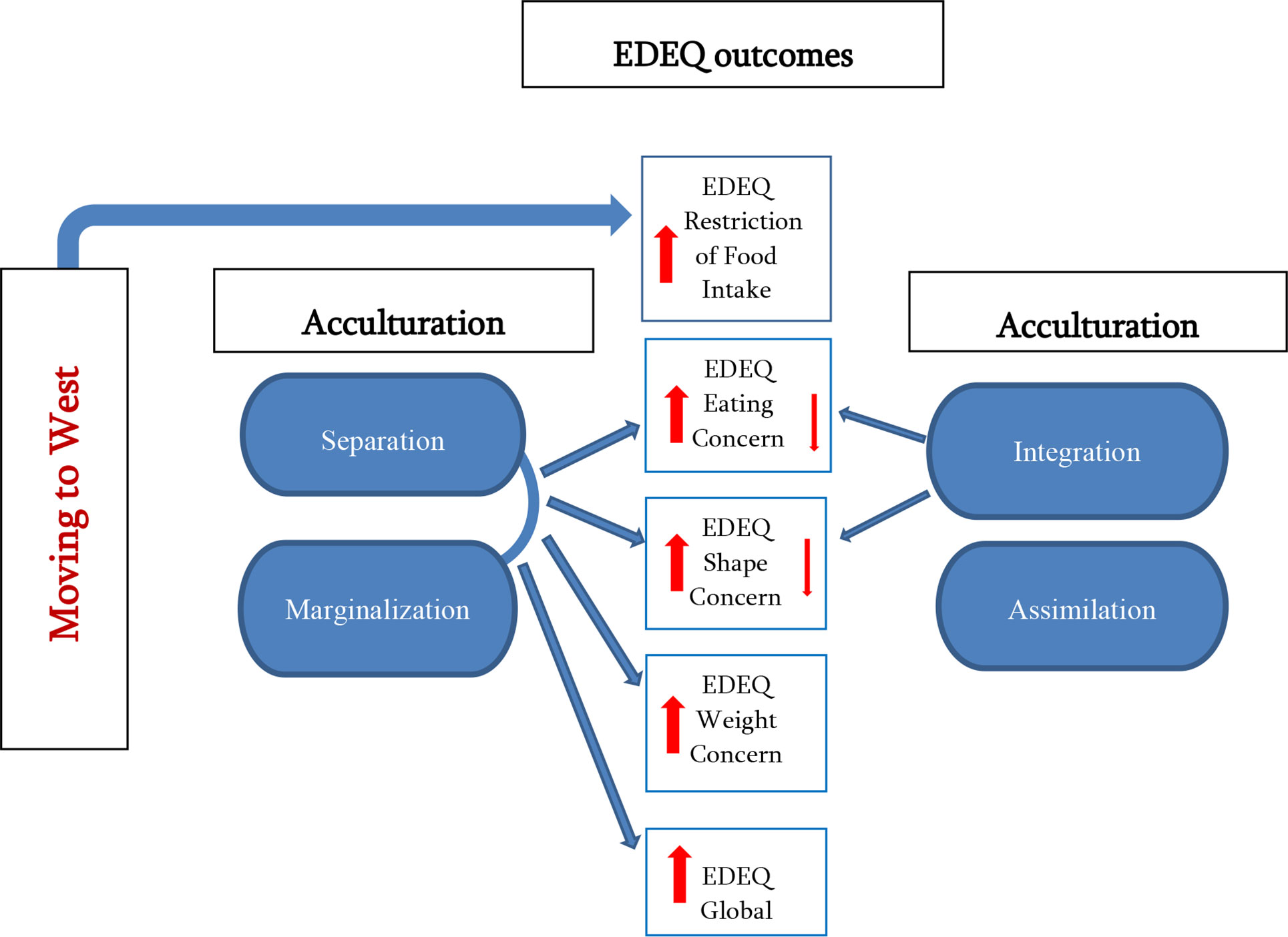
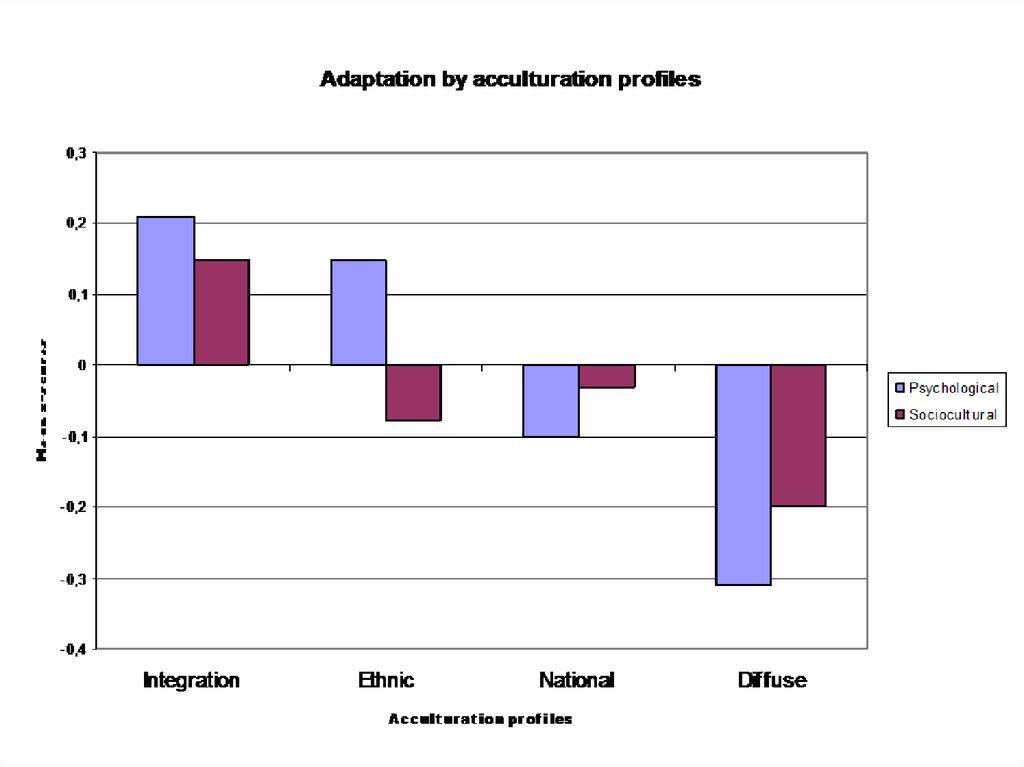
Frontiers Culture Change And Eating Patterns A Study Of Georgian Women Psychiatry
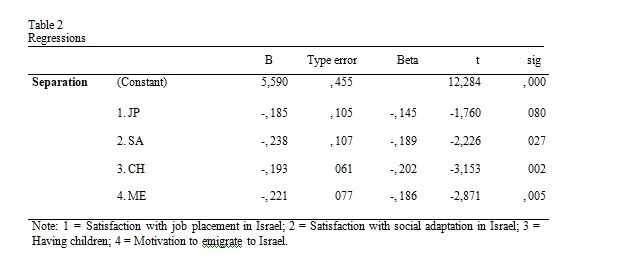
Visor Redalyc Acculturation In Jewish Argentines Migrating To Israel
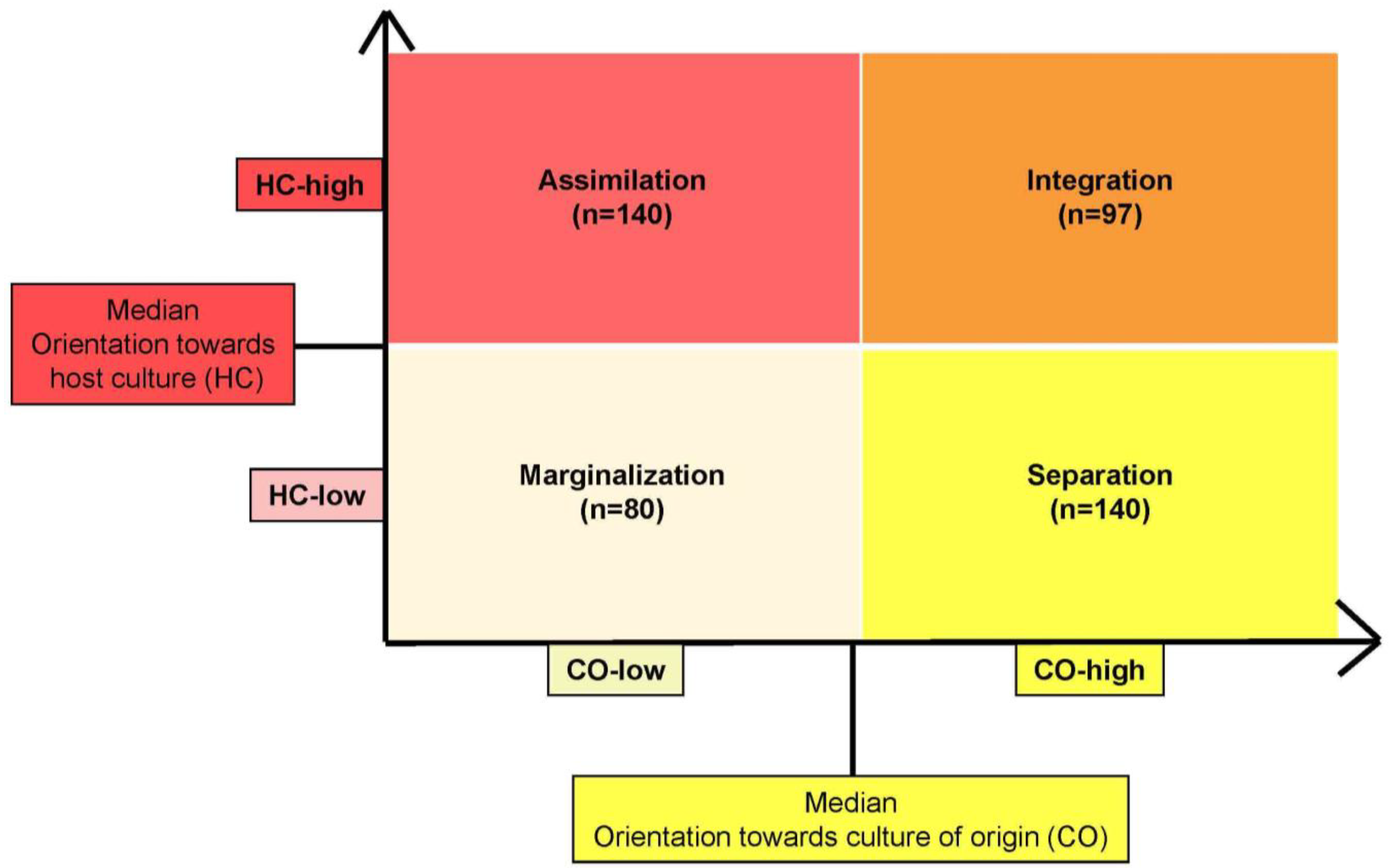
Ijerph Free Full Text Acculturation And Depressive Symptoms Among Turkish Immigrants In Germany Html
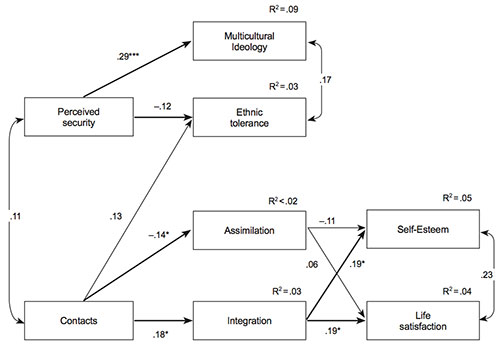
Assimilation Or Integration Similarities And Differences Between Acculturation Attitudes Of Migrants From Central Asia And Russians In Central Russia Psychology In Russia State Of The Art

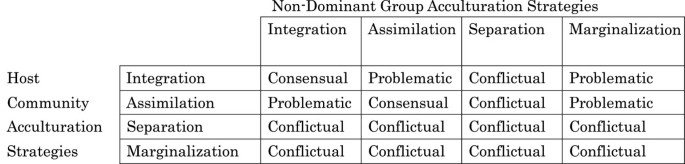
Acculturation Strategies In Ethnocultural Groups And The Larger Society Download Scientific Diagram

Cfs 4 Midterm Diagram Quizlet

Tourists Strategies An Acculturation Approach Sciencedirect

Hispanic Acculturation Processes Evidence Against Assimilation Acr
Towards A Framework For Understanding Ethnic Consumers Acculturation Strategies In A Multicultural Environment A Food Consumption Perspective Emerald Insight
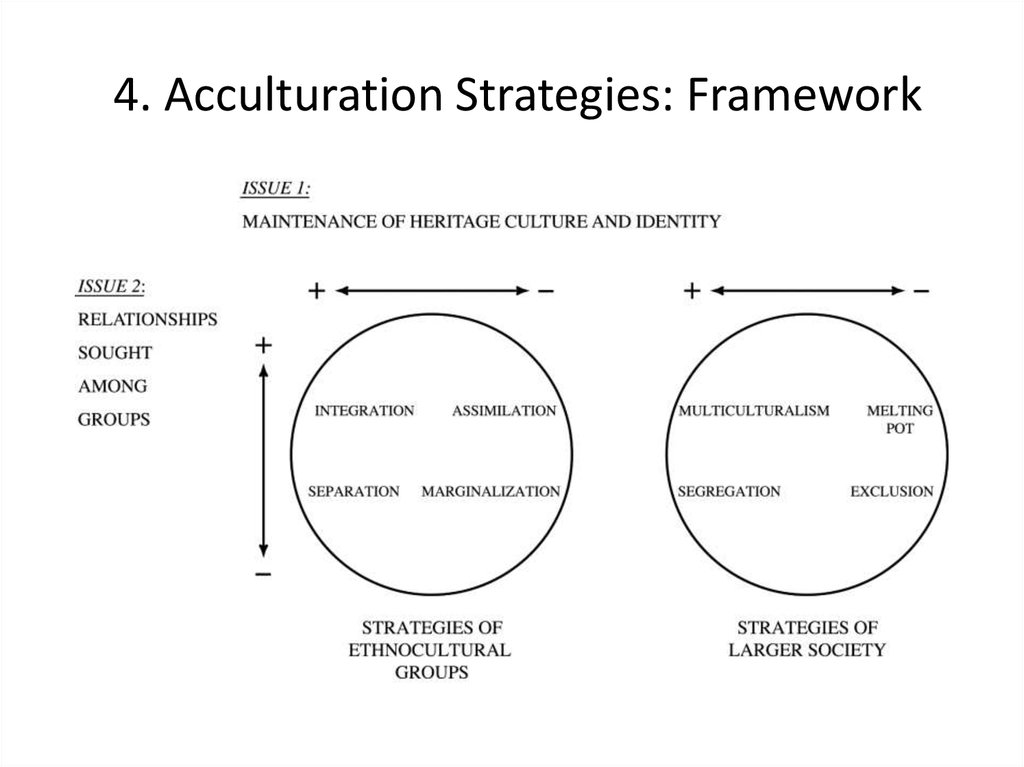
Acculturation And Intercultural Psychology Online Presentation
Gale Academic Onefile Document L Acculturation Et La Migration Des Milleniaux Un Cadre De Congruence Culturelle

Contexts Ofacculturation Chapter 3 The Cambridge Handbook Of Acculturation Psychology

Acculturation And Identity Chapter 16 Textbook Of Cultural Psychiatry




